 |
Cheat Engine
The Official Site of Cheat Engine
|
| View previous topic :: View next topic |
| Author |
Message |
mettaursp
How do I cheat?
![]() Reputation: 0 Reputation: 0
Joined: 02 Aug 2013
Posts: 6
|
 Posted: Sun Aug 11, 2013 6:34 pm Post subject: memscan_firstScan Problem Posted: Sun Aug 11, 2013 6:34 pm Post subject: memscan_firstScan Problem |
 |
|
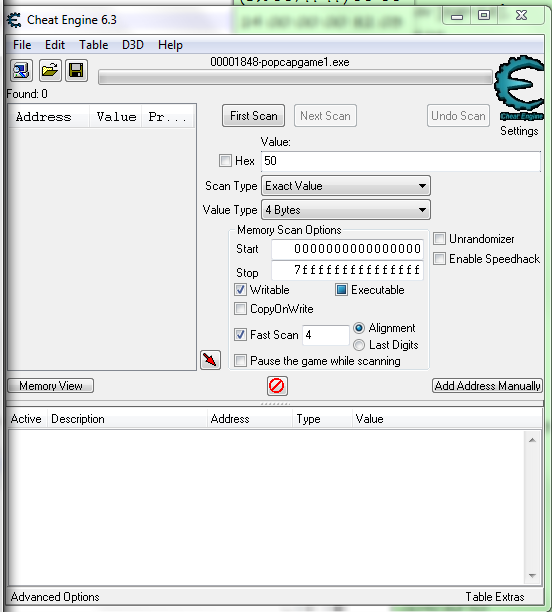
I am trying to make a scanner that finds the sun value in Plants vs. Zombies (original) by using memscan_firstScan and I can't find out how to use a scan with a value type of 4 Bytes. I currently have | Code: | | memscan_firstScan(scanner,1,0,2,"50",nil,0,0xFFFFFFFFFF,"+W*X",0,"",true,false,false,false) |
and that scans single byte values. I know how to find the sun manually, and I am able to find the correct value in 2-3 scans usually. Here are the settings:
Hex - false
Scan Type - Exact Value
Value Type - 4 Bytes
Value - 50 (starting sun)
Also, while I am here, what is the function that retrieves the results of the scan? I should only need one scan because I can already check the opcode to see if it is "xor al,[eax]", which is what all active sun values have as their opcode. Any suggestions?
| Description: |
|
| Filesize: |
66.17 KB |
| Viewed: |
13364 Time(s) |
|
|
|
| Back to top |
|
 |
Dark Byte
Site Admin
 Reputation: 472 Reputation: 472
Joined: 09 May 2003
Posts: 25880
Location: The netherlands
|
 Posted: Sun Aug 11, 2013 7:34 pm Post subject: Posted: Sun Aug 11, 2013 7:34 pm Post subject: |
 |
|
change the second parameter from 0 to vtDword
To get the results create a foundlist object attached to the memscan. then when the scan has finished (use waitTillDone() ) initialize the foundlist and read through the Address list
| Code: |
MemScan Class (Inheritance: Object)
getCurrentMemscan() : Returns the current memory scan object. If tabs are used the current tab's memscan object
createMemScan(progressbar OPTIONAL) : Returns a new MemScan class object
properties
FoundList: FoundList - The foundlist currently attached to this memscan object
OnlyOneResult: boolean - If this is set to true memscan will stop scanning after having found the first result, and written the address to "Result"
Result: Integer - If OnlyOneResult is used this will contain the address after a scan has finished
methods
firstScan(scanoption, vartype, roundingtype, input1, input2 ,startAddress ,stopAddress ,protectionflags ,alignmenttype ,"alignmentparam" ,isHexadecimalInput ,isNotABinaryString, isunicodescan, iscasesensitive);
Does an initial scan.
memscan: The MemScan object created with createMemScan
scanOption: Defines what type of scan is done. Valid values for firstscan are:
soUnknownValue: Unknown initial value scan
soExactValue: Exact Value scan
soValueBetween: Value between scan
soBiggerThan: Bigger than ... scan
soSmallerThan: smaller than ... scan
vartype: Defines the variable type. Valid variable types are:
vtByte
vtWord 2 bytes
vtDword 4 bytes
vtQword 8 bytes
vtSingle float
vtDouble
vtString
vtByteArray
vtGrouped
vtBinary
vtAll
roundingtype: Defined the way scans for exact value floating points are handled
rtRounded : Normal rounded scans. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.49999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.0499999999
rtTruncated: Truncated algoritm. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.099999999
rtExtremerounded: Rounded Extreme. If exact value = "3" then it includes 2.0000001 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 2.900000001 to 3.099999999
input1: If required by the scanoption this is a string of the given variable type
input2: If requires by the scanoption this is the secondary input
startAddress : The start address to scan from. You want to set this to 0
stopAddress : The address the scan should stop at. (You want to set this to 0xffffffffffffffff)
protectionflags : See aobscan about protectionflags
alignmenttype : Scan alignment type. Valid options are:
fsmNotAligned : No alignment check
fsmAligned : The address must be dividable by the value in alignmentparam
fsmLastDigits : The last digits of the address must end with the digits provided by alignmentparam
alignmentparam : String that holds the alignment parameter.
isHexadecimalInput: When true this will handle the input field as a hexadecimal string else decimal
isNotABinaryString: When true and the varType is vtBinary this will handle the input field as a decimal instead of a binary string
isunicodescan: When true and the vartype is vtString this will do a unicode (utf16) string scan else normal utf8 string
iscasesensitive : When true and the vartype is vtString this check if the case matches
nextScan(scanoption, roundingtype, input1,input2, isHexadecimalInput, isNotABinaryString, isunicodescan, iscasesensitive, ispercentagescan, savedresultname OPTIONAL);
Does a next scan based on the current addresslist and values of the previous scan or values of a saved scan
memscan: The MemScan object that has previously done a first scan
scanoption:
soExactValue: Exact Value scan
soValueBetween: Value between scan
soBiggerThan: Bigger than ... scan
soSmallerThan: smaller than ... scan
soIncreasedValue: Increased value scan
soIncreasedValueBy: Increased value by scan
soDecreasedValue: Decreased value scan
soDecreasedValueBy: Decreased value by scan
soChanged: Changed value scan
soUnchanged: Unchanged value scan
roundingtype: Defined the way scans for exact value floating points are handled
rtRounded : Normal rounded scans. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.49999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.0499999999
rtTruncated: Truncated algoritm. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.099999999
rtExtremerounded: Rounded Extreme. If exact value = "3" then it includes 2.0000001 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 2.900000001 to 3.099999999
input1: If required by the scanoption this is a string of the given variable type
input2: If requires by the scanoption this is the secondary input
isHexadecimalInput: When true this will handle the input field as a hexadecimal string else decimal
isNotABinaryString: When true and the varType is vtBinary this will handle the input field as a decimal instead of a binary string
isunicodescan: When true and the vartype is vtString this will do a unicode (utf16) string scan else normal utf8 string
iscasesensitive : When true and the vartype is vtString this check if the case matches
ispercentage: When true and the scanoption is of type soValueBetween, soIncreasedValueBy or soDecreasedValueBy will cause CE to do a precentage scan instead of a normal value scan
savedResultName: String that holds the name of a saved result list that should be compared against. First scan is called "FIRST"
newscan() : Clears the current results
waitTillDone() : Waits for the memscan thread(s) to finish scanning. Always use this
saveCurrentResults(name) : Save the current scanresults to a unique name for this memscan. This save can be used to compare against in a subsequent next scan
getAttachedFoundlist() : Returns a FoundList object if one is attached to this scanresults. Returns nil otherwise
setOnlyOneResult(state): If set to true before you start a scan, this will cause the scanner to only return one result. Note that it does not work with a foundlist
getOnlyResult(): Only works if returnOnlyOneResult is true. Returns nil if not found, else returns the address that was found (integer)
FoundList
The foundlist is an object that opens the current memscan's result file and provides an interface for reading out the addresses
createFoundList(memscan)
properties
Count: integer;
Address[index]
Value[index]
methods
initialize() : Call this when a memscan has finished scanning. This will open the results for reading
deinitialize() : Release the results
getCount()
getAddress(index) : Returns the address as a string
getValue(index) : Returs the value as a string
|
_________________
Do not ask me about online cheats. I don't know any and wont help finding them.
Like my help? Join me on Patreon so i can keep helping |
|
| Back to top |
|
 |
mettaursp
How do I cheat?
![]() Reputation: 0 Reputation: 0
Joined: 02 Aug 2013
Posts: 6
|
 Posted: Sun Aug 11, 2013 7:41 pm Post subject: Posted: Sun Aug 11, 2013 7:41 pm Post subject: |
 |
|
| Thanks, and turns out 50 was in hex so I was ending up with values of 80 in the scan results, so I had to switch 50 with 32. Now just to make sure that the sure that the script identifies the correct value. Btw, is there any Lua function to write to an opcode, and is there a Lua function to do what "Find out what writes to/accesses this address" does?
|
|
| Back to top |
|
 |
|
|
You cannot post new topics in this forum
You cannot reply to topics in this forum
You cannot edit your posts in this forum
You cannot delete your posts in this forum
You cannot vote in polls in this forum
You cannot attach files in this forum
You can download files in this forum
|
|

 Reputation: 472
Reputation: 472

